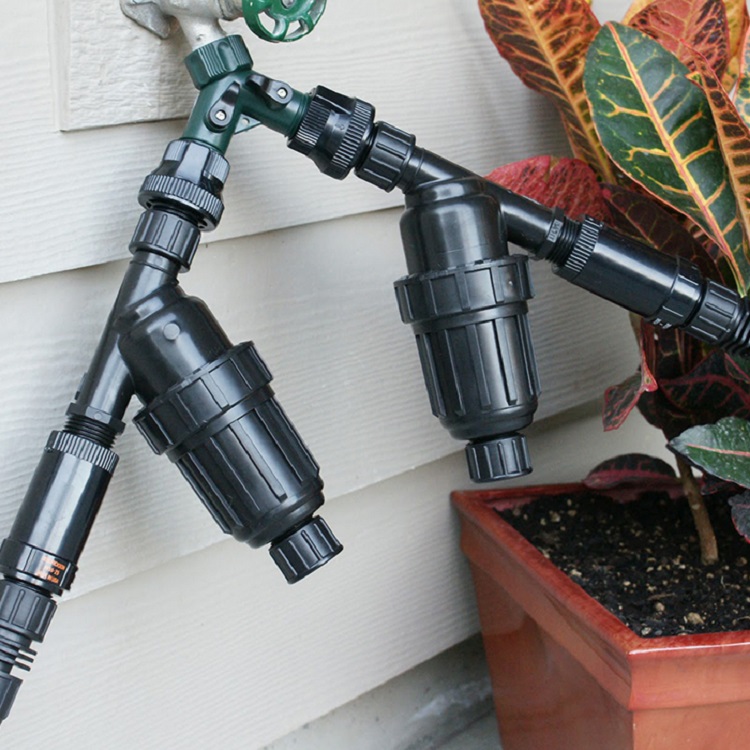
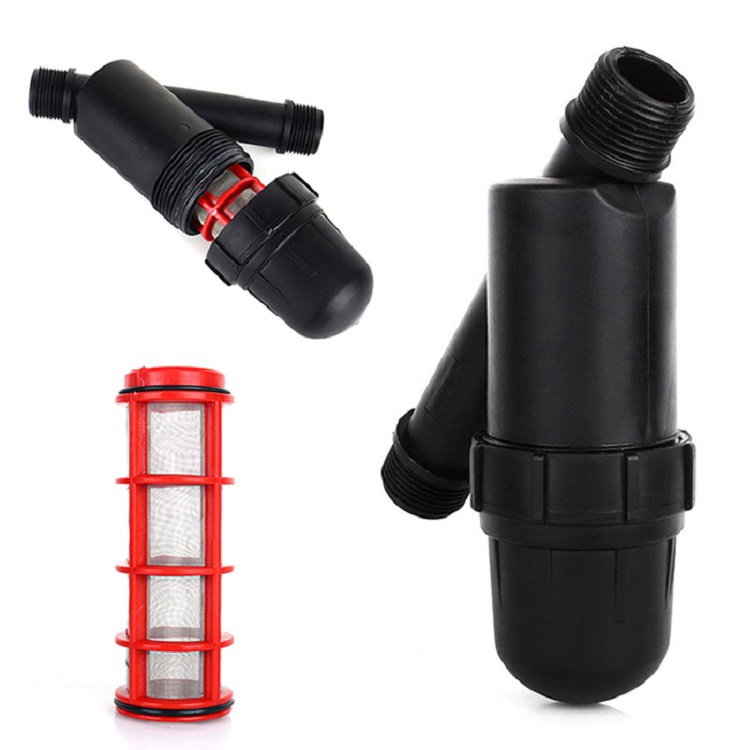
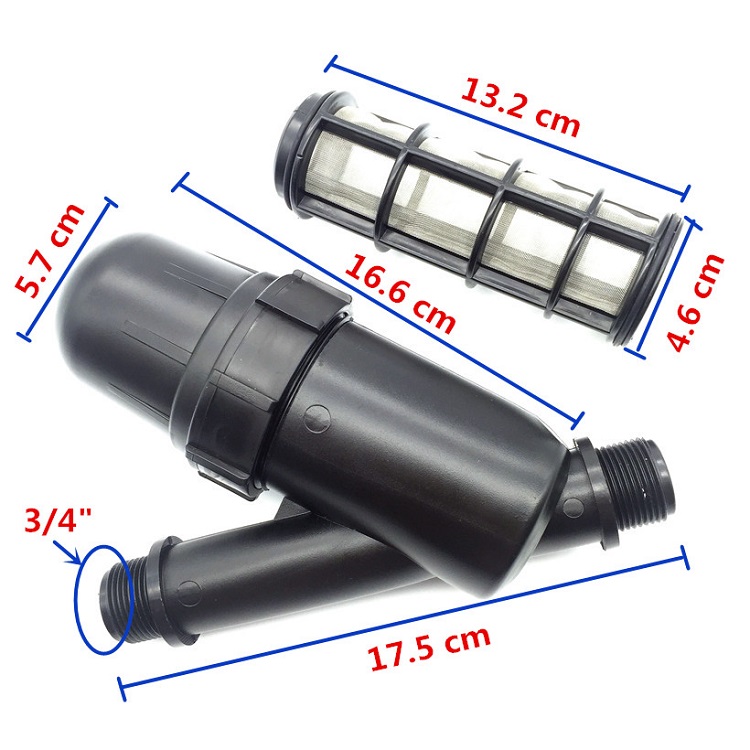
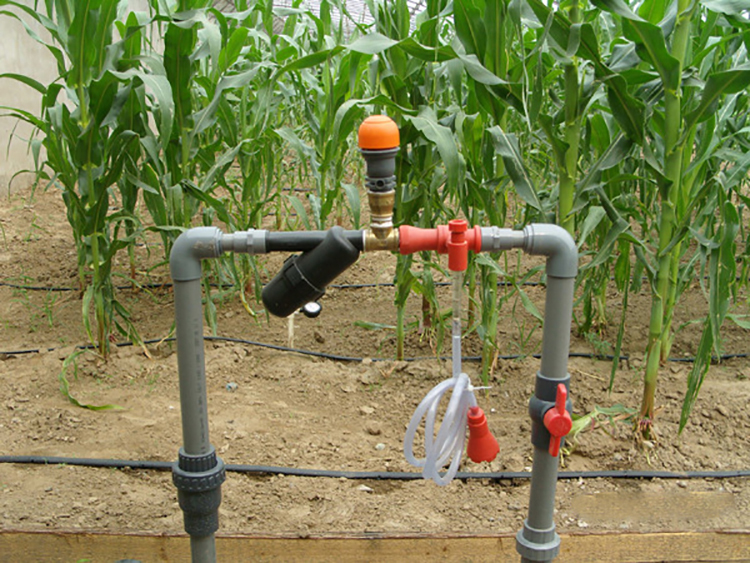
Drip irrigation is a type of irrigation system that involves slowly dripping water directly to the roots of plants through a network of pipes, tubes, and emitters. This method of irrigation is more efficient and effective than traditional irrigation systems because it delivers water directly to the plants’ root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
In drip irrigation, water is supplied to the plants at a slow and steady rate, which allows the soil to absorb the water more effectively. This helps to prevent soil erosion and nutrient loss, as well as reducing water waste. Drip irrigation systems can be used to irrigate a wide range of crops, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and trees.
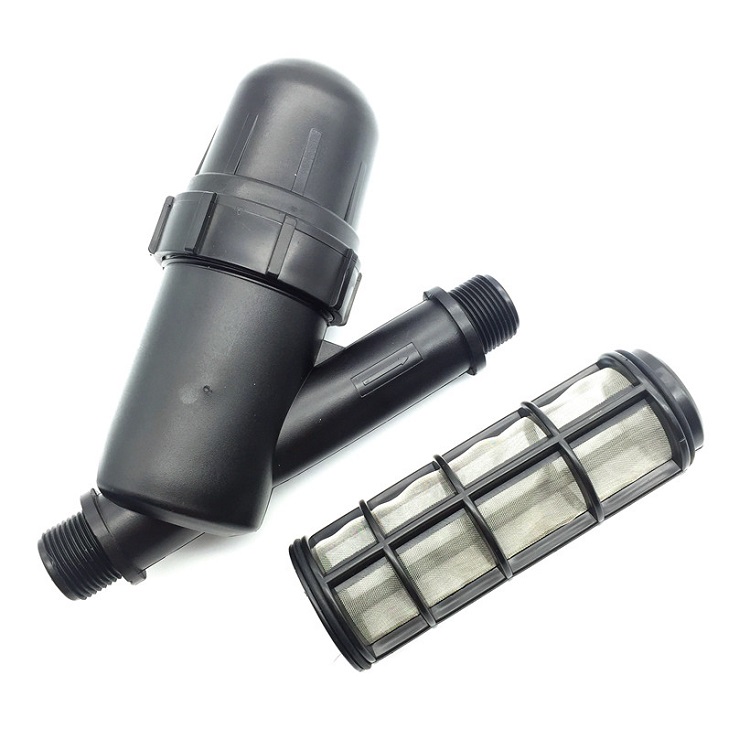
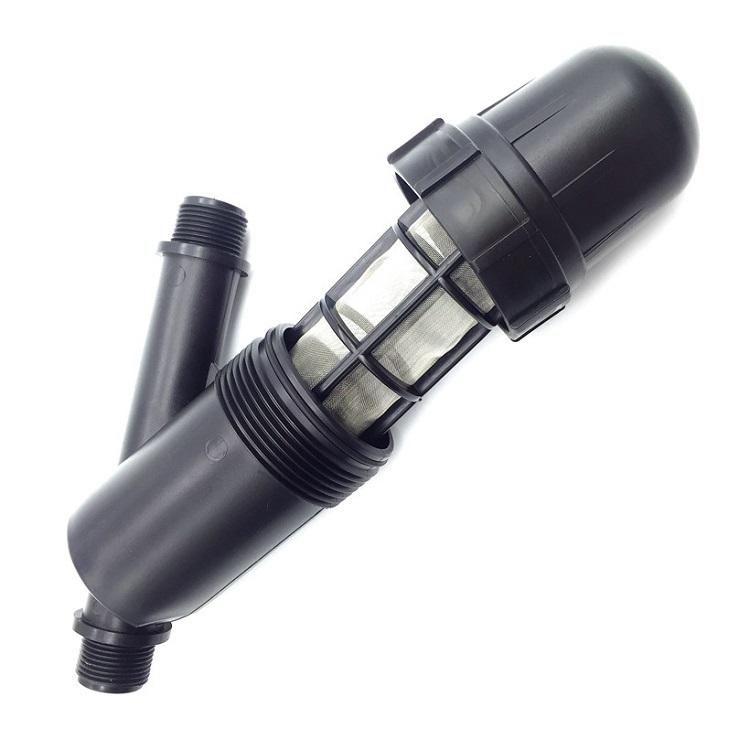
The components of a drip irrigation system include a water source, a filter to remove debris, a pressure regulator to ensure the proper flow of water, tubing or piping to transport water to the plants, and emitters or drip heads to deliver water to the plants. Drip irrigation systems can be designed to be automated, so that water is delivered to the plants at specific intervals throughout the day.
One of the major advantages of drip irrigation is that it uses significantly less water than other irrigation methods, which can result in significant water savings and lower water bills. Additionally, drip irrigation can improve crop yields and quality by providing a more consistent and controlled water supply to plants. Overall, drip irrigation is a highly effective and efficient way to irrigate crops and gardens, and is becoming increasingly popular in both commercial and residential settings.